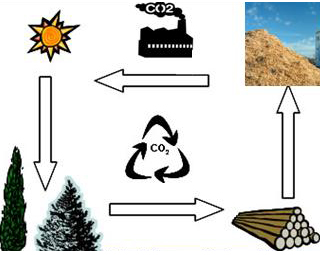
What are pellets?
Pellets or agglomerates of wood are environmentally friendly, wood-based or biomass-based fuel. They are mainly made of sawdust or other waste from wood processing plants. . In many cases they are also produced by alternative biomass raw materials, such as juniper, energy crops, tree trunks (olive trees) and crop residues.
How are they produced?
The process for the production of “wood pellets” includes the following steps:
1. storage of raw materials (biomass) in a clean and dry place.
2. Dry it to reduce its moisture content.
3. cutting and milling it.
4. cooling and sifting of the product produced.
5. pressing it in a special press.
6. storage of the final fuel produced in a safe place.
A prerequisite throughout this process is that the raw material consists exclusively of pure wood, without any other chemical impurities (paints, varnishes, etc.) At the same time, no chemicals are used at their production, as their adhesive gives their compact form, is lignin, a natural substance contained in the wood. Any change in pellet production conditions (insufficient drying for example) results in inferior product quality with lower energy efficiency.
Characteristics
 Wood pellets have a small, cylindrical shape and smooth exterior surface. Their usual dimensions are 1 to 3 cm in length and their diameter 6 to 10 mm. These features give them fluid properties (great flow convenience). Therefore, storage and transport are much easier and more efficient than any other type of wood. The basic feature of the pellet is its very low humidity, its low ash content and its high energy density. All of these features make it an extremely attractive and efficient fuel. According to the European Standard of Quality “EN 14961-2”, which sets strict limits on their properties, wood pellets are divided into three categories: A1, A2 and B. The strictest specifications correspond to the grade A1 wood pellets, which are of excellent quality fuel and ideal for domestic consumption.
Wood pellets have a small, cylindrical shape and smooth exterior surface. Their usual dimensions are 1 to 3 cm in length and their diameter 6 to 10 mm. These features give them fluid properties (great flow convenience). Therefore, storage and transport are much easier and more efficient than any other type of wood. The basic feature of the pellet is its very low humidity, its low ash content and its high energy density. All of these features make it an extremely attractive and efficient fuel. According to the European Standard of Quality “EN 14961-2”, which sets strict limits on their properties, wood pellets are divided into three categories: A1, A2 and B. The strictest specifications correspond to the grade A1 wood pellets, which are of excellent quality fuel and ideal for domestic consumption.
Advantages
1. They don’t contribute to the increase of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The balance between natural wood rot and it’s burning is the same.
2. Their size is small and can be standardized, packed and transported easily.
3. They have low concentration in water and in ash.
4. Burn in suitable stoves – boilers of high quality, with fully automated options.
5. Their cost is low (220-280 euros / ton).
6. Their calorific power is relatively large (4.063 – 4.541 Kcal / Kg)
Why choose a pellet device?
Even if it was possible to guarantee the quality and natural heat from a wood stove or a wood energy save fireplace, pellet appliances , use as a fuel a renewable energy source – whose production is primarily due to wood residues that are compressed – thus avoiding the cutting of new trees with direct consequence the respect of the environment. The pellets do not contain any additional chemicals and are non-toxic. It is an ecological fuel because it is made from natural products such as wood remnants, wood peels and sawdust. Nowadays, these byproducts provide us with renewable energy, whereas in the past the timber factories and the carpenters were a problem because they had to dispose large quantities of these residues as rubbish.
Today, trying to avoid fossil fuels and turning to more eco-friendly heating, such as pellets, the heating costs drop significantly to 60%. Compared to wood, pellets provide higher heating power due to their compressed form, have a very low moisture content, are a cleaner fuel in use and storage. The power of a pellet device is higher when compared to a wood stove or fireplace and the heat output is also more continuous because of the electronic control systems used.
Comparison
| WOODEN STOVE | WOODEN PELLET | |
| ecological burden |
|
Pellets are made from by-products of wood processing which otherwise would not be of any use. |
| Ventilation | A chimney is required to ventilate the stove. | √ Ability of ventilation can be carried out by a limited hole on the wall. |
| Fuel availability | √ Woods are widely available in both urban and non-urban areas. | The necessity of processing the appropriate wood by-products to produce, them automatically makes them less available than wood. |
| Need for electricity | √ Most wood stoves are completely independent of electricity. | Most Pellet stoves require power to operate. |
| Reload of the stove with fuel | Reloading is more frequent and is always done by the user | √ They are equipped with suitable tanks in which the fuel is stored so that its flow is automatic, so increasing the autonomy and reducing the reloading rate by the user |
| Automatic start / stop of a stove | Does not support this function. With the help of a digital programmer it is possible to determine the automatic start and stop of the stove. | √ With the help of a digital programmer, the automatic start and stop of the stove can be determined. |
| Fuel Storage | √ Woods can be stored outside | The pellets must be stored in a room without moisture (inside) because the increase in volume (do to moisture absorption) can cause a malfunction in the stove. |
The devices
In the Greek market, pelllets are used to operate either inside the house (fireplaces or pellet stoves) or even in the boiler room (pellet boilers). Pellet stoves can be either hydraulic stoves (for connection to radiator heaters) or air heaters (the built-in fan advances the produced hot air).
Their operation (indicative):
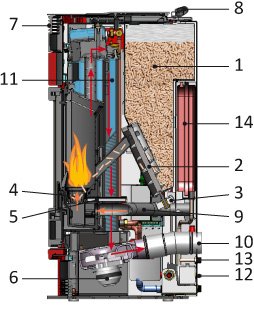
 1 = pellet tank with overhead loading port
1 = pellet tank with overhead loading port
2 = pellet transfer cochlea from the fuel tank to the combustion chamber
3 = operating motor of the cochlea
4 = pellet combustion burner
5 = electrical switch for the first ignition of the pellet
6 = smoke exhaust ventilator
7 = smoke outlet for chimney connection
8 = digital display for settings and display all operating phases
9 = external air intake duct required for combustion
10 = alternating tubes for the production of hot-air heating
11 = front diffuser louver for dispersing hot air in the stove’s operating area
12 = ports for the connection of hot air ducts for its transport to other spaces
13 = fan for hot air diffusion
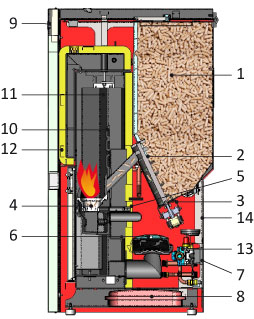
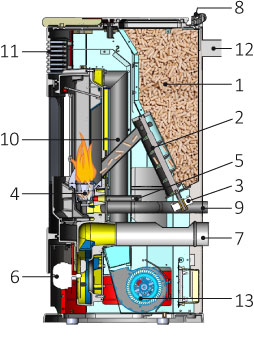
1 = pellet tank with overhead loading port
2 = pellet transfer cochlea from the fuel tank to the combustion chamber
3 = operating motor of the cochlea
4 = pellet combustion burner
5 = electrical switch for the first ignition of the pellet
6 = ventilator for smoke extraction
7 = louver for possible diffusion of hot air into the installation area
8 = digital display for managing and displaying all operating phases
9 = external air supply connection required for combustion
10 = smoke exit port for connection to the chimney
11 = pipes for the circulation and heating of water
12 = water outlet toward the heating network
13 = return from the heating network
14 = closed expansion container
boiler